Plasma Pipe Cutting Compensation
Do you want to improve your plasma pipe cutting accuracy? Are your cut parts too short or are your cuts not straight? Which side of the plasma should you use to get a better cutting quality? There are a few ways to improve plasma cutting accuracy significantly. In this article below you find three ways to improve your plasma pipe cutting accuracy.
Kerf Width Compensation
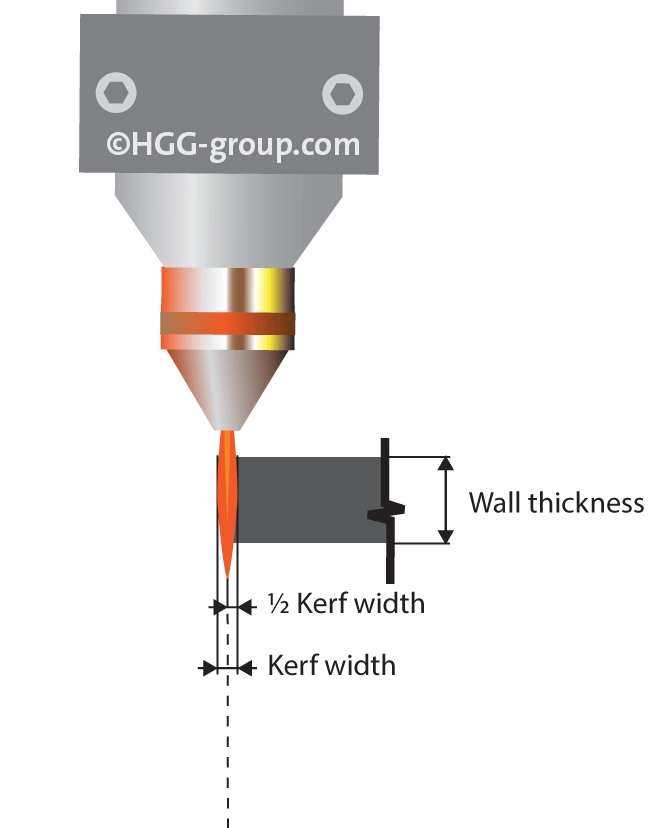
The width or kerf is dependent on the plasma source, voltage, and amperage based on the wall thickness. To ensure an even better accuracy, this kerf can be compensated by a pipe cutting machine’scontrol software. This compensation is typically half of the kerf width.
Kerf Width Compensation
The width or kerf is dependent on the plasma source, voltage, and amperage based on the wall thickness. To ensure an even better accuracy, this kerf can be compensated by a pipe cutting machine’s, such as HGG’s SPC 500 – 1200 PT, control software. This compensation is typically half of the kerf width.
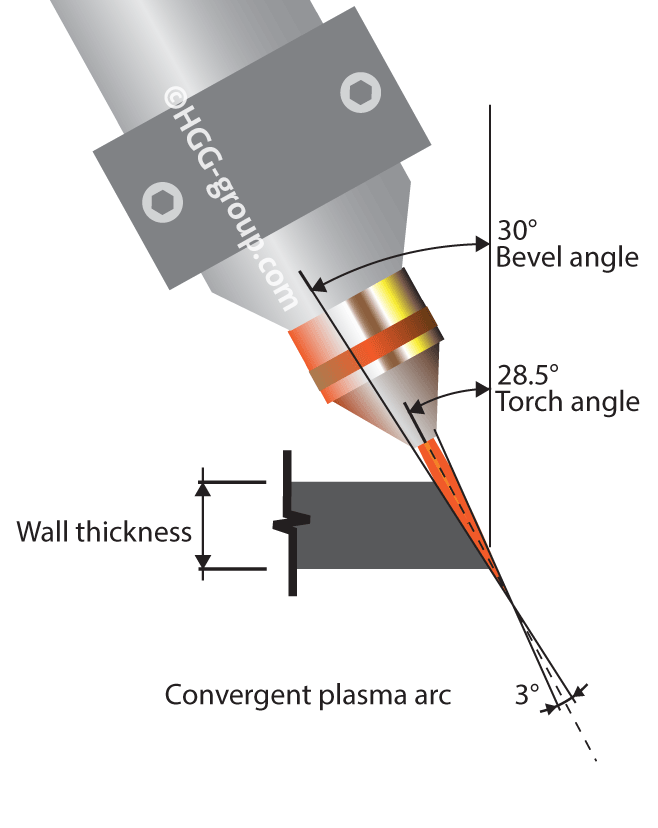
Divergence Compensation
In most cutting conditions the plasma beam is divergent; this divergence can vary depending on the plasma torch and nozzle. To make sure the cutting angle is accurate the divergence compensation can be reprogrammed into the machine as an offset. As an example, if the divergence of the beam is 3 degrees and the required bevel of 30 degrees, the cutting angle is has an offset of 1.5 degrees. Consequently, setting torch is 31.5 degrees compensating the divergence.
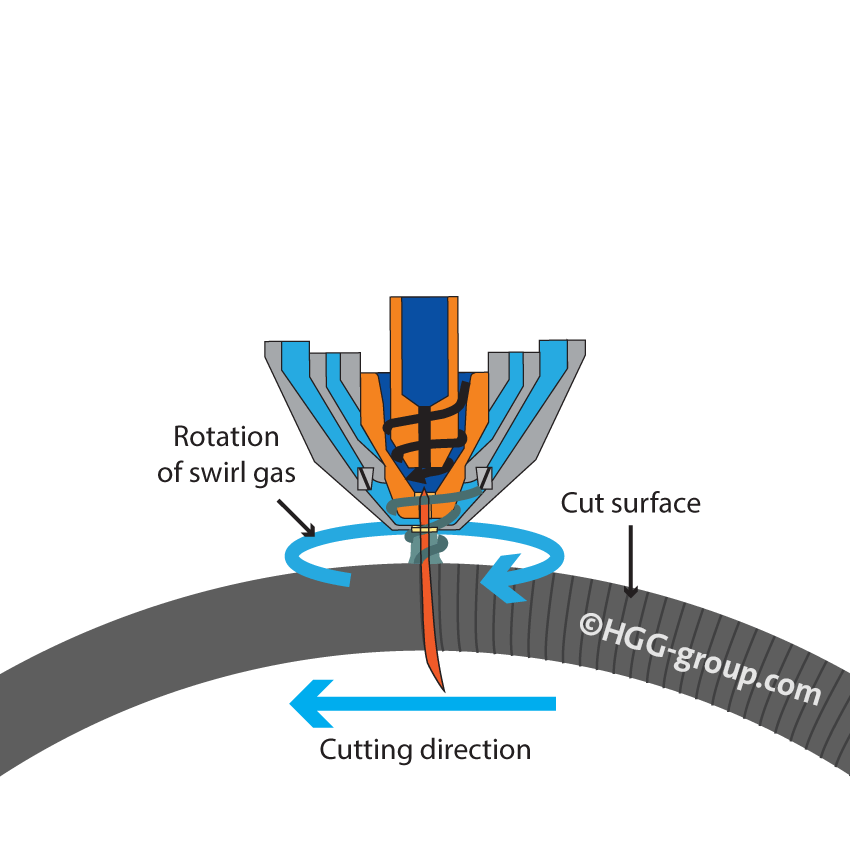
Optimized Cutting Direction
Plasma cutting uses a swirl to focus, stabilize and protect the beam firmly. In order to get a straight cut on your production pieces you must travel in the proper direction. The “good side” is on the right as the torch is travelling away from you.